The residential sector consists of private households. Energy is consumed primarily for space heating, water heating, air conditioning, refrigeration, cooking, clothes drying, and lighting. Fuel used for motor vehicles by household members is included in the transportation sector.
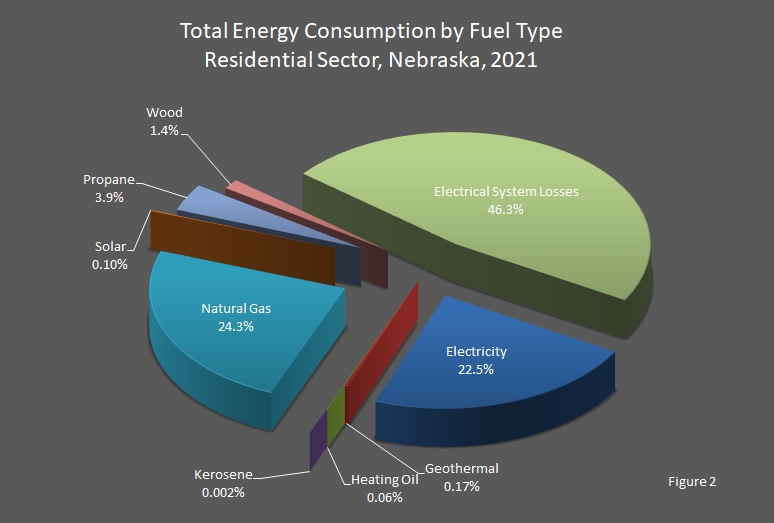
For the residential, commercial, and industrial sectors, a net total or net energy consumption (less electrical system energy losses) is provided to indicate the energy actually consumed by these sectors. In addition, energy consumed in the generation, transmission, and distribution of electricity (electrical system energy losses) is allocated to each sector based on the electricity consumed by the sector. Thus, total energy consumption represents the energy consumed by the sector as well as that used to provide electricity to the sector.
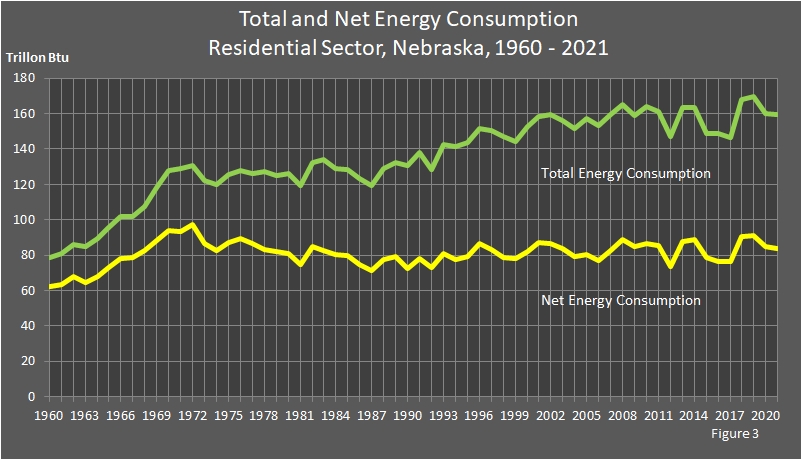
Between 2020 and 2021, residential sector net energy use decreased 1.31 percent to 83.5 trillion British thermal units (Btu), which was 14.1 percent below the peak of 97.2 trillion Btu recorded in 1972. Total energy consumption attributed to the residential sector in 2021 was 159.3 trillion Btu, an decrease of 0.5 percent from 2020. Petroleum use decreased 3.8 percent, natural gas use decreased 2.1 percent, and electricity use decreased 0.2 percent. Renewable energy use increased 1.8 percent from 2020. Coal consumption remained at a level low enough to round to zero.
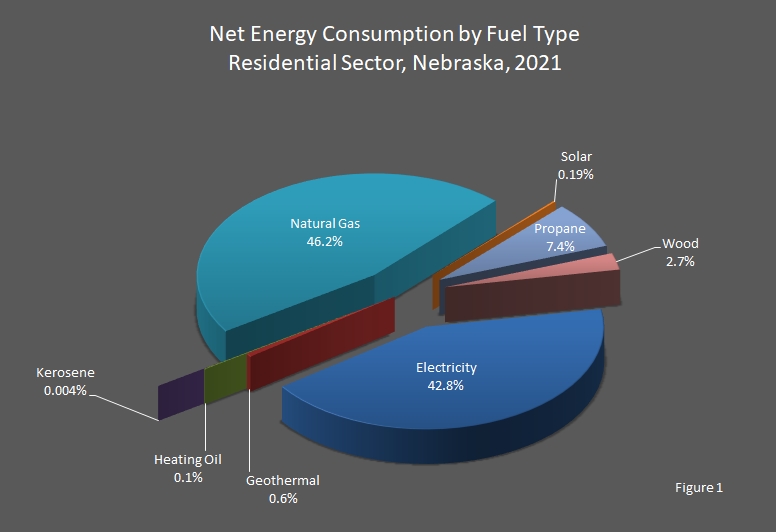
In 2021, 46.2 percent of the residential sector's energy needs were met by natural gas. Forty–two and eight–tenths percent (42.8%) of the energy consumed in the residential sector was electricity, 6.3 percent were petroleum products, and 2.9 percent was renewable energy. According to the 2021 American Community Survey, 59 percent of Nebraska's households used natural gas for home heating, 32 percent used electricity, 7 percent used propane, 0.3 percent used heating oil, and 0.004 percent used coal.