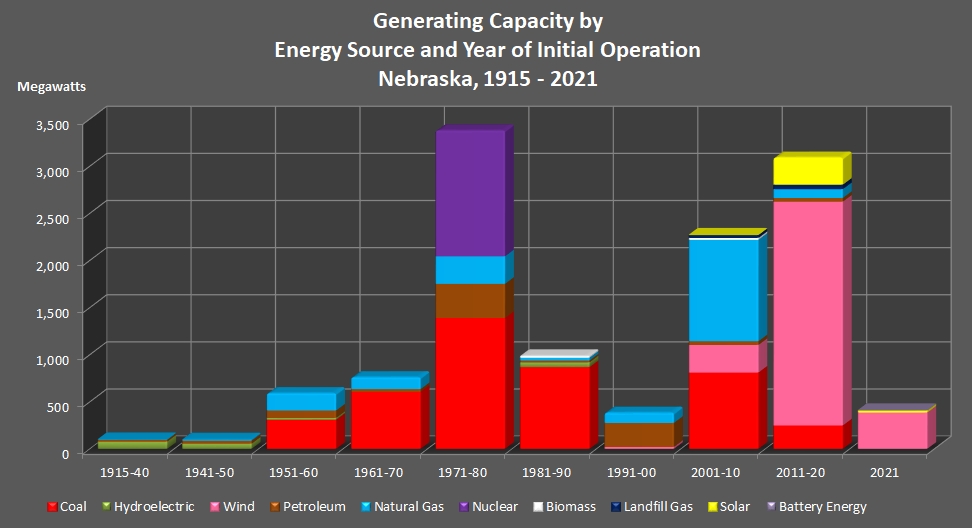
This report shows the new generation that became commercially operable from 1915 to 1940 and then during each decade since then. Details about the generation includes energy source, number of units/wind turbines, the nameplate capacity, the summer capacity, and the winter capacity.
From 1915 to 1970, an increasing number of new units were brought on line each ten–year period.
A record of 73 units started up in the period of 1951–1960. With half as many new units (37) than 1951–1960, the 1971–1980 period had the biggest increase in capacity (3,379.7 megawatts). Nuclear power accounted for almost half of the capacity added that period. Also, all nuclear power was started up in that period.
Also see the Units and Capacity by Energy Source report and the Generating Units report for additional information.
A Note About Nameplate Capacity
Summer capacity and winter capacity is sometimes greater than nameplate capacity. The nameplate gives the capacity rating of the generator when it operates at certain temperatures, pressures, and power factors. With some modifications and with some margins that are built into generators, it is possible to exceed its nameplate. It is not uncommon for a generator to exceed its nameplate. The nameplate is usually not replaced and, in this case, the summer and winter capacity is often much higher than the nameplate value. Normally, you expect summer and winter capacity to be below nameplate capacity and in most cases they are.